-
Home
-
Product Center
-
Application
-
Support
-
JT Cloud
-
About Us
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

In today's fast-paced work environments, ensuring employee safety has become a paramount concern for organizations across the globe. One critical aspect of workplace safety is the effective management of environmental conditions, particularly temperature control. The Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) Monitoring system is an indispensable tool that helps measure heat stress in the workplace, effectively preventing heat-related illnesses and enhancing overall safety. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), nearly 2,000 American workers suffer heat-related illnesses each year, underlining the dire need for proactive measures in managing heat exposure.
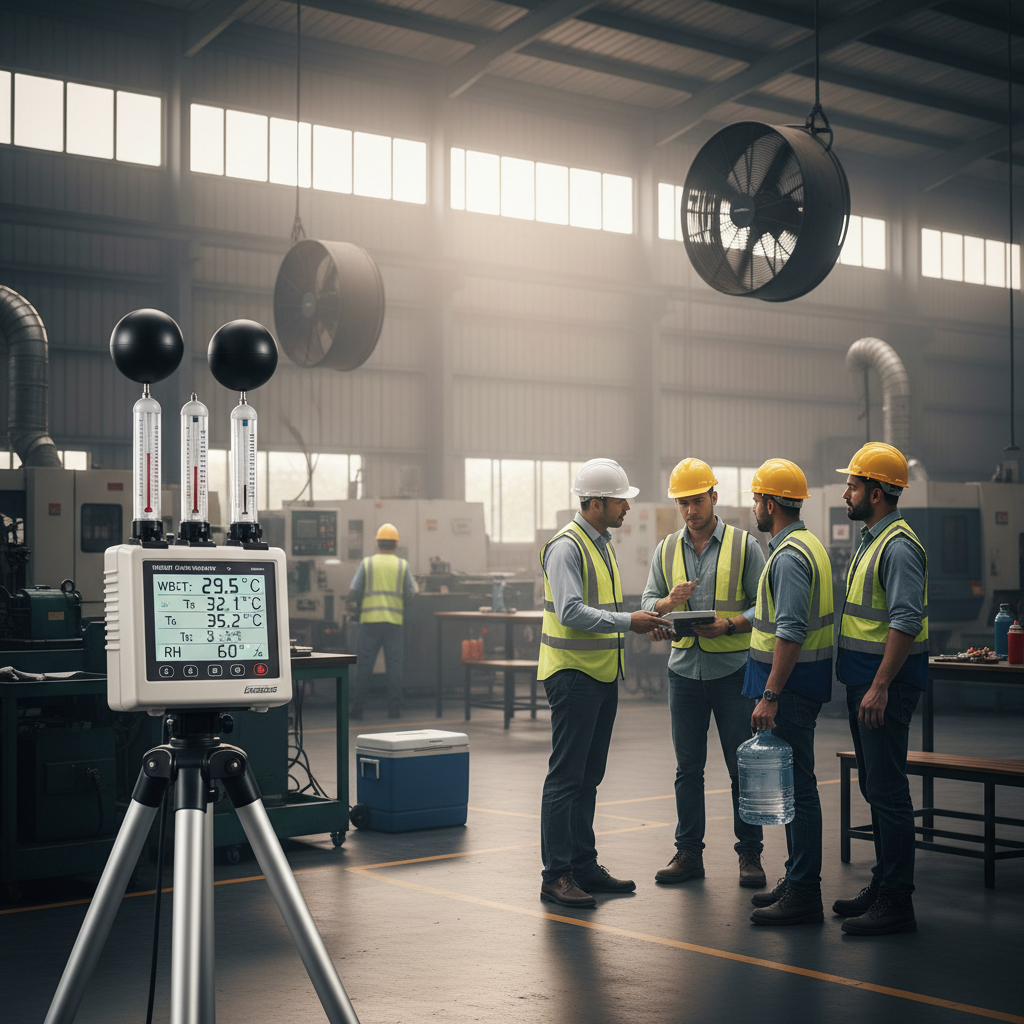

Implementing Wet Bulb Globe Temperature Monitoring not only supports the physical well-being of employees but also promotes productivity and morale. Research from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) emphasizes that effective heat stress management can lead to a significant reduction in workplace accidents and injuries. By accurately measuring humidity, radiant heat, and air temperature, WBGT Monitoring provides employers with actionable insights to make informed decisions regarding work-rest cycles and hydration strategies. Therefore, integrating this advanced monitoring technique becomes essential for organizations aiming to create a safer and more productive work setting, especially as temperatures are projected to rise in the coming years due to climate change.
Wet bulb globe temperature (WBGT) is a crucial metric in evaluating the heat stress an individual may experience in hot environments. It combines humidity, temperature, and solar radiation, providing a comprehensive assessment of thermal stress. According to the American Conference of Governmental and Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH), exposure to high WBGT levels can lead to heat-related illnesses, including heat exhaustion and heat stroke, particularly in outdoor work environments like construction sites and agriculture.
Monitoring WBGT is imperative for workplace safety, especially in industries where workers are exposed to heat for prolonged periods. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) recommends using WBGT readings to set thresholds for work-rest cycles to prevent overheating. For instance, when the WBGT exceeds 85°F (29.4°C), organizations should implement frequent breaks and hydration strategies. This proactive approach not only safeguards employees’ health but can also reduce downtime, as heat-related incidents account for significant losses in productivity, as highlighted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), which estimates that tens of thousands of heat-related illnesses occur annually in the workforce.
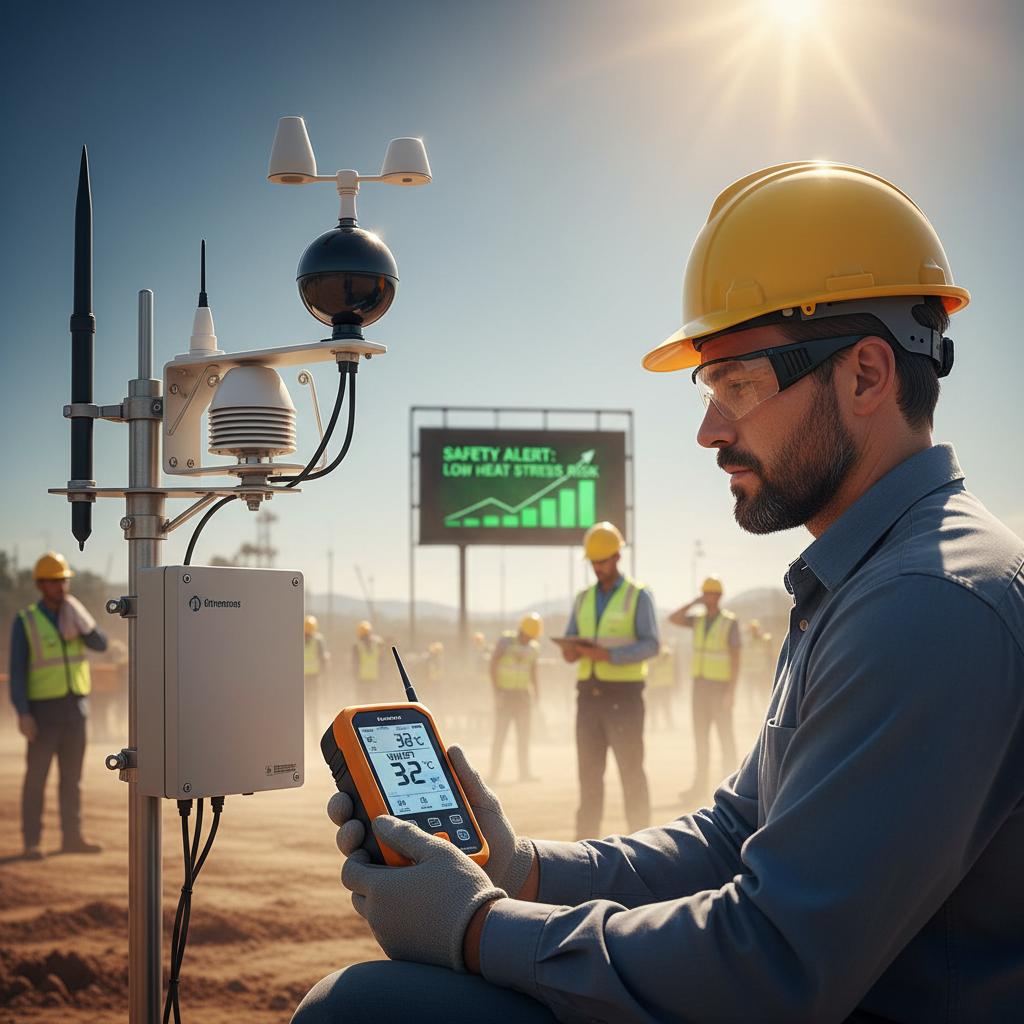

The importance of continuous monitoring for heat stress prevention in workplaces cannot be overstated. The Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) is a key metric that combines temperature, humidity, wind speed, and solar radiation to provide a comprehensive assessment of heat stress risks. Research from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) indicates that extreme heat events may result in a significant rise of heat-related illnesses, leading to decreased productivity and increased healthcare costs. By implementing WBGT monitoring, organizations can proactively address heat stress and safeguard employees' health.
One effective tip is to establish a regular monitoring schedule. According to a study published in the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, continuously measuring WBGT allows employers to adjust work schedules and implement necessary breaks during high-risk periods. Another recommendation is to provide training for employees on recognizing heat stress symptoms and the importance of hydration. The American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) has noted that informed employees are better equipped to handle environmental stressors and can take personal protective measures.
Incorporating real-time WBGT data into your safety protocols can enhance decision-making. Organizations equipped with proper monitoring devices can tailor their safety strategies based on immediate conditions, thus minimizing the risk of heat-related incidents. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) highlights that preventive actions based on precise data can reduce the likelihood of accidents and ultimately create a safer, more productive work environment.
The integration of technology in monitoring workplace conditions has revolutionized safety protocols, particularly through Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) monitoring. Utilizing real-time temperature tracking, organizations can effectively manage heat stress among employees, ensuring a proactive rather than reactive approach to safety. This method employs advanced sensors and IoT devices to gather accurate environmental data, allowing for immediate responses to potentially hazardous conditions. As climates change and extreme weather events become more frequent, the role of technology in maintaining workplace safety will only grow more crucial.
Furthermore, real-time WBGT monitoring can be integrated with broader digital systems, offering enhanced risk management capabilities. Businesses can leverage predictive analytics to anticipate heat-related challenges and create tailored safety measures. By implementing such forward-thinking strategies, companies not only protect their workforce but also foster a culture of safety that encourages employee well-being. As demonstrated in various sectors, including healthcare with smart bed technology and environmental management with AI in wildfire detection, the synergy between intelligent systems and real-time data is pivotal for advancing organizational safety standards.
Training employees on recognizing heat-related risks is crucial in enhancing workplace safety, especially in environments where the Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) is a concern. Employees should be educated about the symptoms of heat stress, such as dizziness, excessive sweating, and heat cramps. By familiarizing staff with these signs, they can take proactive measures to address the situation before it escalates into a more serious condition.
Moreover, training programs should include practical strategies to mitigate heat-related risks. Employees can be taught the importance of staying hydrated, taking regular breaks, and wearing appropriate clothing to regulate body temperature effectively. In addition, organizations can implement simulations and role-playing exercises that allow employees to practice their response to heat emergencies. By equipping workers with the knowledge and skills to recognize and react to heat-related risks, companies not only promote a safer working environment but also foster a culture of safety that values the well-being of every employee.
| Strategy | Description | Benefits | Impact on Safety |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Monitoring | Continuous tracking of heat stress conditions. | Immediate awareness of temperature increases. | Prevents heat-related illnesses. |
| Employee Training | Educating employees on recognizing signs of heat stress. | Empowers workers to act swiftly. | Fosters a proactive safety culture. |
| Heat Risk Assessment | Identifying high-risk areas and activities. | Informs better planning and resource allocation. | Reduces incidences of heat exhaustion. |
| Implementation of Rest Breaks | Structured breaks based on temperature readings. | Ensures adequate recovery time for workers. | Decreases the chance of heat stroke. |
| Utilization of Technology | Using wearable devices for temperature monitoring. | Enhances prompt detection of unsafe conditions. | Improves overall workplace safety. |
Implementing effective response protocols based on Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) monitoring data is essential for enhancing workplace safety, particularly in environments where heat stress is a concern. By closely monitoring WBGT, employers can gain valuable insights into current environmental conditions and take immediate action to mitigate risks. For instance, when measurements indicate high heat levels, managers can enact cooling breaks, adjust work schedules, or provide additional hydration to ensure employees remain safe and productive.
Moreover, data-driven response protocols help create a culture of safety and preparedness. Training employees to recognize the signs of heat-related illnesses and how to respond effectively fosters a proactive approach. Incorporating WBGT monitoring data into safety planning enables organizations to develop tailored strategies that address specific risks associated with their unique work environments. This not only protects workers but also enhances overall operational efficiency, as informed decisions lead to better resource management and reduced absenteeism due to heat-related illnesses.
This chart illustrates the importance of Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) monitoring in enhancing workplace safety by analyzing the effectiveness of different strategies implemented based on WBGT data.