
-
Home
-
Product Center
-
Application
-
Support
-
JT Cloud
-
About Us
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

Architectural design relies heavily on understanding sunlight. "The Sun Simulator Heliodon" is a groundbreaking tool. It helps architects visualize sunlight and shadows in their designs. James Carter, a renowned architect, states, “This tool bridges the gap between ideas and reality.” His insight reflects the importance of accurate sunlight simulation.
Using The Sun Simulator Heliodon, designers can assess natural light effects on structures. They can recreate different times of day and seasonal variations. This enhances planning for energy efficiency and comfort. However, some may overlook the need for consistent adjustments and maintenance of the simulator. Mistakes can lead to miscalculations in design.
Moreover, it is vital to remember that simulation cannot replace real-world testing. The tool offers a preview, but it may not fully represent environmental variables. Architects must stay vigilant about these limitations. Balancing technology with hands-on experience is key.

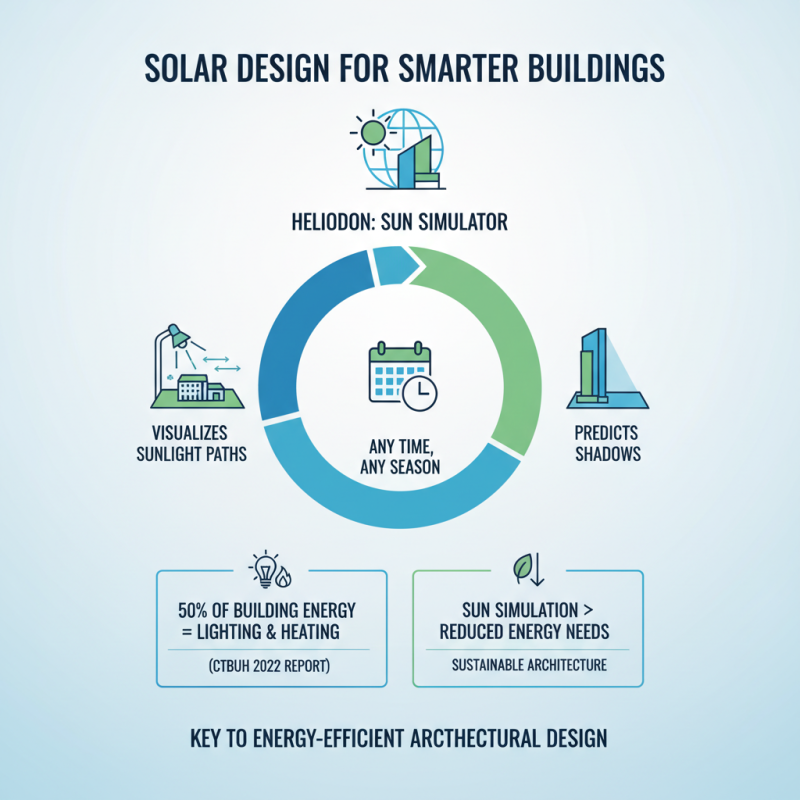
Sun simulation is crucial in architectural design. It helps in understanding how sunlight interacts with buildings. An effective way to visualize this is through a sun simulator heliodon. This tool allows architects to see sunlight paths and shadows at different times of the year. According to a 2022 report by the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat, 50% of energy used in buildings comes from lighting and heating. By using sun simulation, architects can reduce energy needs significantly.
Understanding sun and shadow effects can shape building orientation and window placement. For instance, placing windows towards the south can enhance natural light. A study published in the Journal of Architectural Engineering found that well-placed windows can reduce lighting costs by 30%. However, relying solely on simulations has limitations. Real-world conditions vary, and simulations are based on models. Architects should validate their designs with real-life observations. This ensures that the intended energy efficiency is achieved in actual conditions.
Moreover, short-term simulations might miss long-term seasonal changes. Without considering those, designs may not perform as expected year-round. It's essential to iterate designs based on real feedback. Architectural design is an ongoing learning process. Adapting to the sun's journey is just one piece of the puzzle.
The heliodon is a powerful tool in architectural design, simulating sunlight for various environmental conditions. This device enables designers to visualize how sunlight interacts with structures throughout the day and year. According to a 2022 report by the Architectural Research Institute, nearly 70% of architects who utilize heliodon data report improved energy efficiency in their projects.
Using a heliodon effectively requires understanding its functions. Designers can adjust the angle and intensity of the light to mimic different times of day or seasons. This helps in studying shadows and light penetration in buildings. However, many users often overlook the importance of accounting for local topography in their simulations. A failure to do so can lead to inaccurate assessments of sunlight exposure.
Incorporating heliodon data into early design phases is crucial. Research shows that up to 40% of energy loss in buildings can be attributed to improper daylighting strategies. By addressing these issues, designers can make informed decisions. A well-utilized heliodon can bridge the gap between aesthetic appeal and functionality in architecture, but only if its limitations are understood.
Setting up a Sun Simulator Heliodon is a vital step for accurate architectural design. Begin by ensuring you have a stable, flat surface. This will support the simulator and provide reliable results. Place architectural models on the platform. Ensure they are correctly oriented with respect to their intended site location.
Next, set up the light source. Position it to simulate the sun's rays at various times of day. Be aware that the angle of light significantly affects shadow casting on your models. Use a protractor to find the correct angles for different times of the year. Adjust the height of the light source to mimic seasonal variations.
Tips: Create a checklist before the setup. This helps avoid missing critical steps. Keep a camera handy. Document your findings for future reference and improvements. Don't expect perfection the first time. Shadow patterns may reveal flaws in design. Study these details and adjust accordingly. The goal is to enhance the project through this iterative process.
Using a sun simulator like the Heliodon can significantly enhance architectural design.
This tool helps architects visualize solar effects on their models. For example, it allows designers to observe sunlight patterns
at different times of the day. Reports indicate that buildings optimized for natural light
can reduce energy costs by up to 30%. Yet, many architects overlook this vital step.
Analyzing how sunlight interacts with structures is crucial. Shadows can affect both visual aesthetics and energy efficiency.
Studies suggest that 60% of energy use in buildings comes from heating and cooling.
Architects need to consider these factors early in the design process. Observing the sun's path helps in making informed decisions.
However, it's common to underutilize this simulation in early design phases.
Some designers struggle to interpret simulation results effectively. The initial data might seem overwhelming, leading to confusion.
Learning to correlate sunlight angles with heat gain can be challenging yet rewarding. Not every design will benefit equally from
this analysis. Recognizing the limitations of each project is essential for better outcomes.
Integrating Heliodon results into sustainable design strategies can enhance architectural projects. Sun simulators help architects visualize light and shadow impacts on buildings. By simulating sunlight, we can analyze how buildings interact with their environment. This process helps optimize natural light use and reduce energy consumption.
Architects often overlook seasonal sunlight variations. Using a Heliodon, one can visualize these changes over different times of the year. For example, summer sun can penetrate deep into spaces while in winter, it might not reach certain areas. This insight is crucial for designing energy-efficient buildings that align with sustainable practices. It allows for better placement of windows and thermal protection.
However, challenges remain. Data from the Heliodon might not fully represent real-world conditions. Architects must combine these results with local climate data. There’s a risk in relying solely on simulations. They provide valuable insights, but real-life execution may vary. Balancing technology with hands-on observations is vital for successful integration.
This chart illustrates the carbon emissions associated with different building orientations based on sun exposure. Using this data can help architects incorporate sustainable design strategies into their projects.





