
-
Home
-
Product Center
-
Application
-
Support
-
JT Cloud
-
About Us
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

In the rapidly evolving landscape of environmental monitoring, the choice of a
Temperature and Humidity Sensor is critical for various applications ranging from industrial processes to home automation.
Renowned expert in environmental technology, Dr. Emily Morgan, emphasizes
the significance of selecting the right sensor by stating,
"Choosing the appropriate Temperature and Humidity Sensor is not just about accuracy; it’s about ensuring the sensor aligns with the specific needs of the application."
As industries increasingly recognize the impact of temperature and humidity on product quality and operational efficiency, the demand for reliable sensors has surged.
Understanding the different types of sensors available and their respective features is essential for making an informed decision.
The correct Temperature and Humidity Sensor can enhance data accuracy, improve system responsiveness, and ultimately save costs.
With various factors such as calibration, range, and response time to consider, this guide delves into the essential criteria for choosing the best
Temperature and Humidity Sensor to meet your specific requirements, ensuring you make a choice that supports both functionality and reliability in your projects.

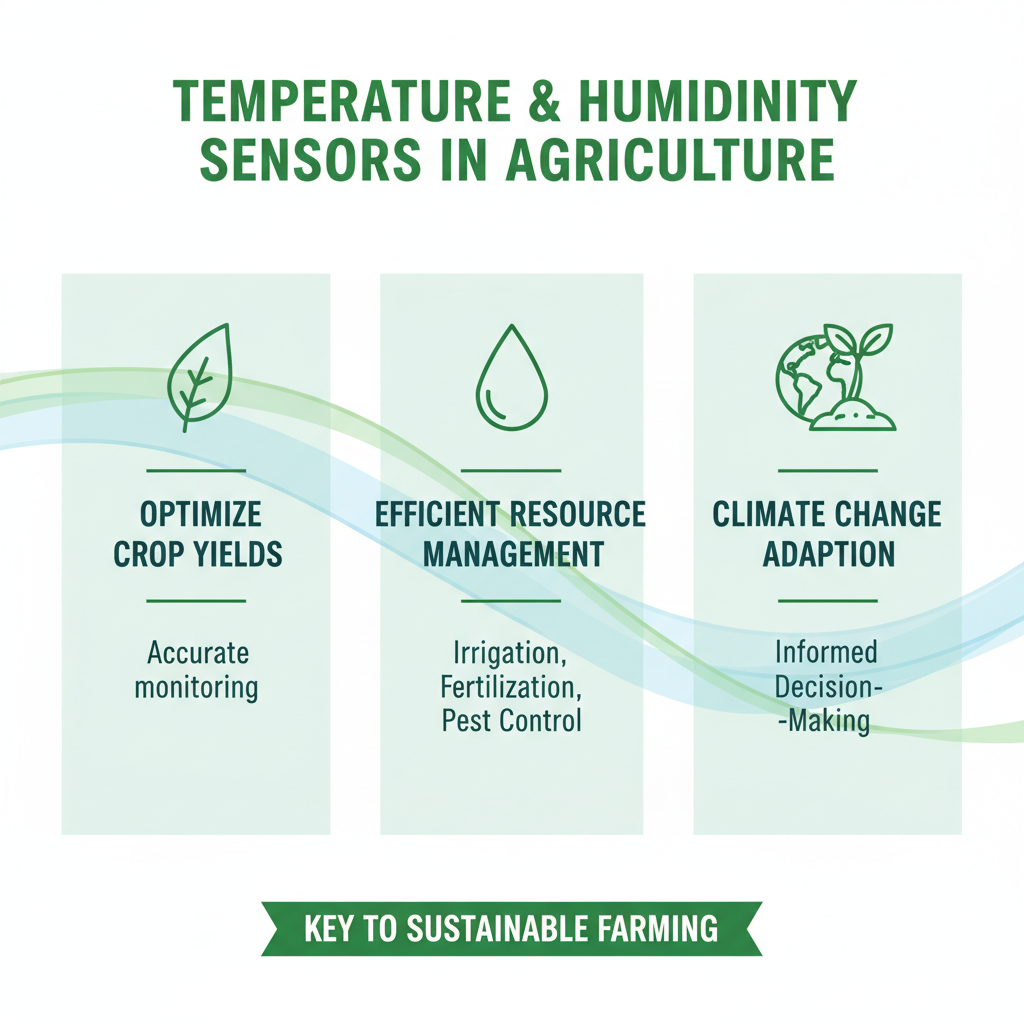
Temperature and humidity sensors play a crucial role in various industries, especially in agriculture, where accurate monitoring is essential for optimizing crop yields and ensuring sustainable practices. The growing demand for precise environmental monitoring, driven by climate change and its unpredictable effects on weather patterns, underscores the need for high-quality sensors. By leveraging advanced technology, these sensors help farmers make informed decisions regarding irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, ultimately leading to more efficient resource management.
The market for temperature and humidity sensors is expected to grow significantly, with projections indicating a rise from $350 million in 2024 to $4.1 billion by 2033. This growth trajectory reflects an annual compound growth rate of 2% from 2025 to 2033. Additionally, the increasing adoption of IoT (Internet of Things) solutions for environmental monitoring further amplifies the urgency for reliable sensor networks. By integrating various types of sensors—including soil moisture, air flow, and light sensors—agricultural stakeholders can create a comprehensive monitoring system that responds dynamically to environmental changes, ensuring optimal conditions for crops and livestock.
When selecting a temperature and humidity sensor, understanding the various types available can greatly influence your choice. There are primarily three types of sensors:
capacitive, resistive, and thermal.
Capacitive sensors measure humidity by detecting changes in capacitance in a hygroscopic material. They are known for their accuracy and wide range of measurement but can be more expensive.
Resistive sensors, on the other hand, operate by measuring the change in electrical resistance of a hygroscopic material. While they tend to be less accurate than capacitive types, they are often cost-effective and reliable for basic applications.
Thermal sensors, also called hygrometers, measure humidity based on the cooling effect of evaporation. These sensors are typically used in environments where high precision is not critical but quick response times are necessary.
In addition to these types, factors like operating range, response time, and calibration are essential in choosing the right sensor for your specific requirements.
Understanding these differences will help you make an informed decision that meets your project's unique needs.
When selecting a temperature and humidity sensor, it's crucial to consider key features that directly impact performance. One of the primary features is the sensor's accuracy, which can vary between ±0.1°C to ±1°C for temperature and ±1% to ±5% for humidity, depending on the model. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global market for environmental sensors is expected to reach $5.3 billion by 2024, highlighting the increasing importance of precision in these devices.
Another vital aspect to evaluate is the sensor's response time. A quicker response time allows for more real-time monitoring and effective regulation of temperature and humidity levels, essential in applications like greenhouse management or HVAC systems. Many advanced sensors boast response times under 2 seconds, as reiterated by a study from ResearchAndMarkets, which emphasizes the growing demand for rapid and reliable data acquisition.
**Tips:** Always assess the sensor's compatibility with existing systems to ensure seamless integration. Additionally, consider sensors with built-in data logging capabilities, as they can provide historical insights and aid in predictive maintenance. Lastly, evaluate the sensor’s environmental rating, ensuring it can withstand the specific conditions of its intended application.
| Feature | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Range | The range of temperature and humidity that can be measured | -40°C to 125°C, 0% to 100% RH |
| Accuracy | How close the sensor's readings are to the true values | ±0.5°C, ±2% RH |
| Response Time | Time taken for the sensor to reach a stable reading | <5 seconds |
| Output Signal | Type of signal the sensor outputs for data communication | Analog (0-10V), Digital (I2C, RS232) |
| Power Supply | Voltage and current requirements for sensor operation | 5V DC, 20mA |
| Calibration | Process for adjusting the sensor for accurate measurements | Factory calibrated, user calibration option available |
| Size | Physical dimensions of the sensor | 50mm x 30mm x 15mm |
When selecting a temperature and humidity sensor, evaluating accuracy and calibration standards is crucial. High-quality sensors often specify their accuracy in terms of a percentage of the reading, such as ±0.5°C for temperature and ±2% RH for humidity. According to a report by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), maintaining stringent calibration standards can significantly reduce measurement errors, thus ensuring the reliability of environmental monitoring.
Tips:
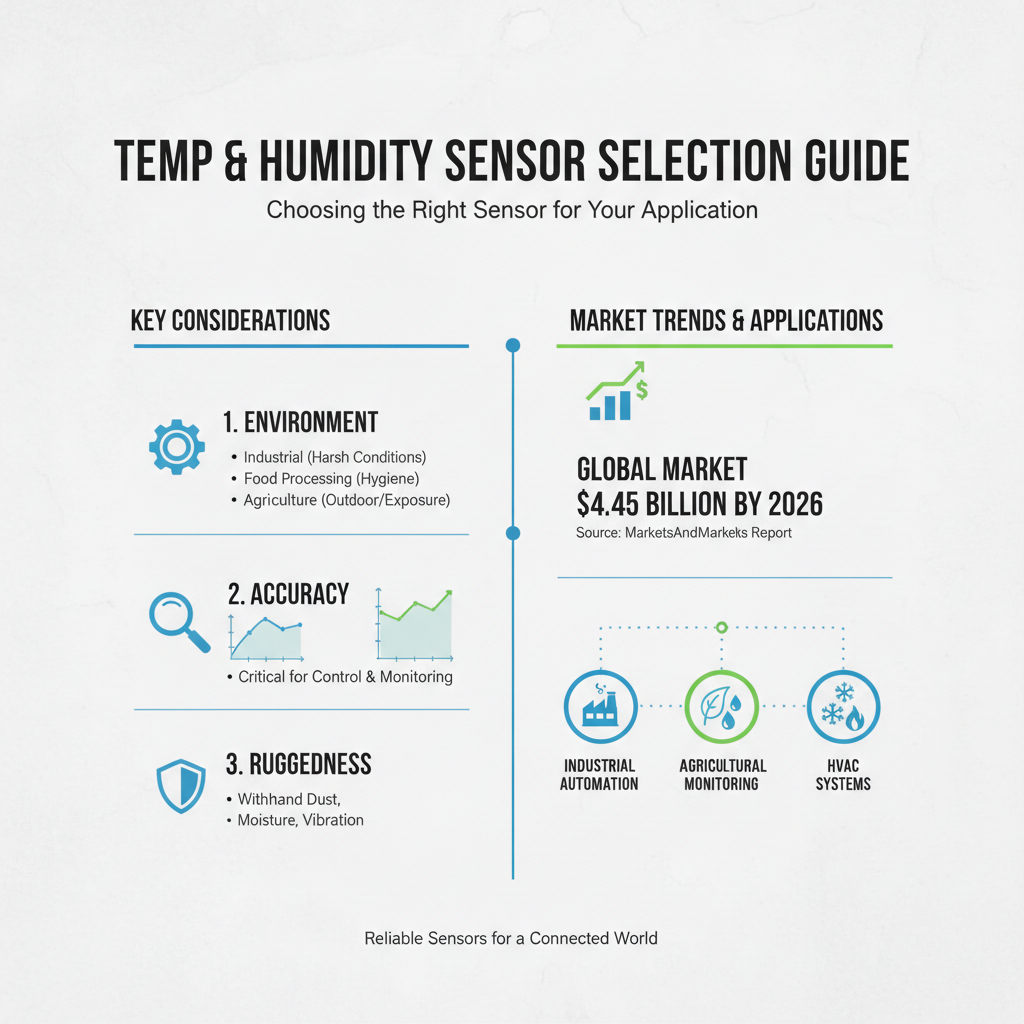
When selecting the right temperature and humidity sensor for specific applications, it's crucial to consider the environment in which the sensor will operate. For instance, industrial settings often require sensors with higher accuracy and ruggedness to withstand harsh conditions.
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global temperature and humidity sensor market is projected to reach $4.45 billion by 2026, highlighting the growing demand for reliable sensors in diverse applications like food processing, HVAC systems, and agricultural monitoring.
In controlled environments like laboratories or cleanrooms, precision is paramount. Sensors used in these settings typically need to have a response time under 1 second and an accuracy level of ±0.5°C and ±2% RH, as specified by the International Society for Calibration in Temperature and Humidity Measurement. Choosing sensors that meet these standards can prevent costly errors and ensure optimal performance.
Additionally, sensors with digital outputs and connectivity features are becoming increasingly essential, as they allow for real-time monitoring and data logging, enhancing operational efficiency and decision-making in applications requiring strict environmental controls.





