
-
Home
-
Product Center
-
Application
-
Support
-
JT Cloud
-
About Us
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

In an era where environmental safety and health consciousness are paramount, understanding the importance of a Radiation Monitor has never been more crucial. Individuals and organizations alike are increasingly aware of potential radiation exposure in various settings, from medical facilities to industrial sites. The right radiation monitoring device can serve as an essential tool for detecting and measuring radiation levels, ensuring that safety standards are met and maintained.
Choosing the best Radiation Monitor involves considering several factors tailored to your specific safety needs. It is vital to assess the type of radiation you may encounter, whether it be alpha, beta, gamma, or x-ray. Additionally, the context in which the monitor will be used—be it for personal safety, occupational health, or emergency response—should heavily influence your decision-making process. Furthermore, understanding the monitor's sensitivity, accuracy, and ease of use can significantly enhance its effectiveness in ensuring safety.
In this guide, we will explore the key considerations to keep in mind while selecting a Radiation Monitor that aligns with your safety requirements. By the end, you will be equipped with the knowledge necessary to make an informed choice, enhancing your protection against radiation exposure in everyday life and specific professional environments.

When choosing a radiation monitor, it’s essential to understand the different types available and their specific uses to ensure optimal safety. There are primarily three types of radiation monitors: alpha, beta, and gamma detectors. Alpha radiation monitors are designed to detect alpha particles, which have a low penetration ability but can be harmful when ingested or inhaled. Beta monitors, on the other hand, measure beta particles that can penetrate skin but are less dangerous externally. Gamma radiation monitors are crucial as they detect high-energy photons that can penetrate the human body, making them vital in environments like nuclear power plants and medical facilities.
According to reports from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), the market for radiation detection instruments is expected to grow significantly, reaching approximately $3.5 billion by 2026, driven by stringent safety regulations and the increasing need for radiation monitoring in various industries. Furthermore, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) stresses the importance of personal dosimeters for individuals working in high-radiation areas, highlighting that these devices provide real-time exposure data to ensure that personnel remain within safe exposure limits. Understanding the functionalities and applications of these monitors is crucial for making informed decisions tailored to specific occupational safety needs.
| Type of Radiation Monitor | Detection Method | Radiation Types Detected | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geiger-Müller Counter | Gas-filled detector | Alpha, Beta, Gamma | Environmental monitoring, Health physics |
| Scintillation Detector | Scintillation material & photomultiplier | Alpha, Beta, Gamma, X-rays | Nuclear medicine, Security screening |
| Dosimeter | Passive detector | Gamma, X-rays | Radiation worker monitoring, Personal safety |
| Ionization Chamber | Air-filled and measures ionization | Alpha, Beta, Gamma | Radiation surveys, Laboratory use |
| Digital Radiation Survey Meter | Combination of multiple technologies | Alpha, Beta, Gamma, X-rays | Emergency response, Site assessments |
When selecting a radiation monitor, it's essential to focus on several key features that ensure your safety needs are met. One of the first aspects to consider is the type of radiation the monitor detects. Different monitors may be designed to detect alpha, beta, and gamma radiation, so it’s crucial to choose one that aligns with your specific environment or exposure risk. Additionally, look for devices that offer a range of detection capabilities, as this can provide a more comprehensive understanding of your exposure.
Another vital feature is the monitor's sensitivity and accuracy. A high-quality radiation monitor should provide precise readings, enabling you to identify dangerous levels of radiation effectively. Consider models that offer a user-friendly interface, allowing you to interpret results quickly and make informed decisions. Finally, battery life and durability are also important; a robust monitor that can withstand various conditions ensures that you are prepared in any situation. With the right features, you can enhance your safety and peace of mind in radiation-prone environments.
When selecting a radiation monitor, evaluating
sensitivity and
precision is crucial to ensuring reliable detection of ionizing radiation.
Sensitivity refers to the ability of a radiation detector to respond to the smallest amounts of radiation,
which is essential for promptly identifying any potential exposure. A highly sensitive monitor can pick up low levels of radiation that might otherwise go unnoticed,
providing an early warning that can be vital for safety. However, sensitivity must be balanced with
precision; a detector that is overly sensitive may trigger false alarms
due to natural background radiation or other benign sources.
Precision relates to a radiation monitor's accuracy
in providing consistent readings across varied conditions. A precise detector will yield similar results under
the same exposure conditions, facilitating effective monitoring and assessment of radiation levels.
When selecting a monitor, consider features such as the calibration process and the technology used in detection, as these elements significantly impact both
sensitivity and
precision of the device. A reliable radiation monitor should offer a good balance of these qualities,
ensuring that users can trust the readings while maintaining safety in environments where exposure to radiation is a concern.
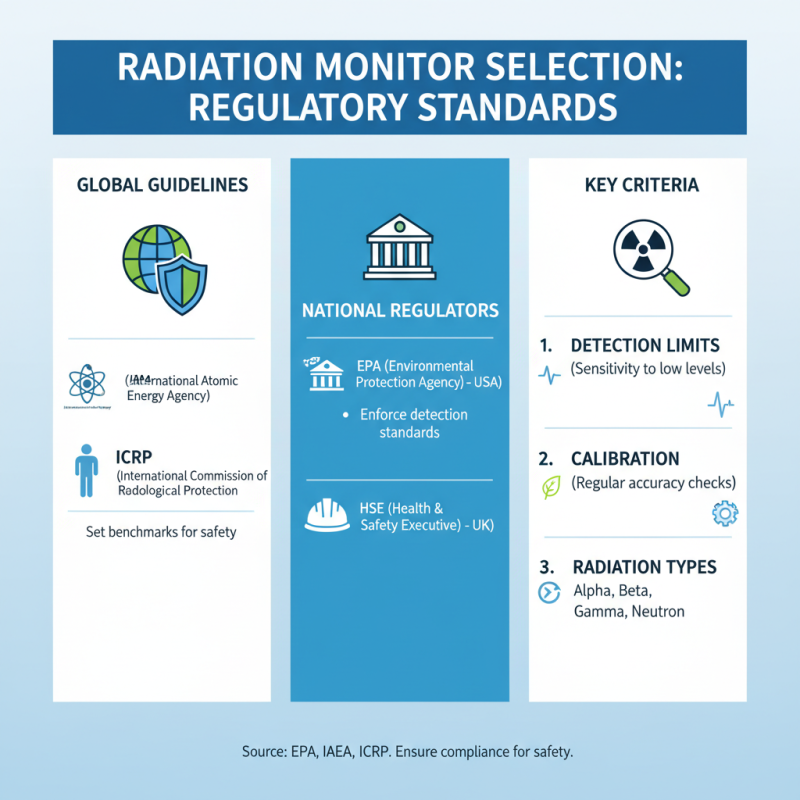
When selecting a radiation monitor, it's crucial to assess the regulatory standards and safety guidelines that determine its effectiveness. Many countries have established regulatory bodies like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) that set the benchmark for safety in radiation detection. These organizations have detailed standards concerning the detection limits, calibration procedures, and overall performance of radiation monitors. For example, the EPA recommends that personal monitoring devices should be sensitive to a range of radiation types, including alpha, beta, and gamma radiation, ensuring comprehensive protection.
Understanding safety guidelines is equally vital. According to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), devices must meet specific criteria to ensure they provide accurate readings and reliable performance under various conditions. Many safety guidelines also require monitors to undergo rigorous testing and certification processes. This regulatory framework not only ensures product quality but also helps consumers make informed choices.
**Tips:** Before purchasing a radiation monitor, verify that it complies with local regulatory standards and certifications. Look for monitors that provide details on their sensitivity and accuracy to enhance your safety. Additionally, consider tools that offer features like real-time monitoring and user-friendly interfaces to make your radiation safety practices more effective.
When selecting a radiation monitor, understanding the balance between cost and functionality is vital to ensure safety without overspending. Low-cost monitors might seem appealing, but their limited features could lead to inadequate protection or important data being overlooked. These basic devices may not differentiate between types of radiation or fail to provide real-time readings, which are essential for effective monitoring.
On the other hand, higher-end models usually offer advanced functionalities like energy discrimination, digital displays, and data logging capabilities. These features enhance the user experience and provide comprehensive insights into radiation levels, making them invaluable for professionals in industries such as healthcare, environmental science, and nuclear energy. However, while investing in a more expensive unit, it’s essential to evaluate if the additional functionalities align with your specific needs. Understanding the intended use case can help optimize the investment, ensuring you obtain a monitor that provides both the necessary protection and the best value for your budget.





